A Thermal Paper Machine plays a crucial role in modern printing technology. It efficiently converts specialized thermal paper into high-quality printed materials. As an expert in the field, Dr. James Lin emphasizes the importance of these machines, stating, "The Thermal Paper Machine revolutionizes the way we print receipts and labels." His insight highlights the machine’s impact on various industries.
The working mechanism of a Thermal Paper Machine is intriguing. It employs heat to transfer ink onto paper, eliminating the need for traditional ink supplies. This method not only reduces costs but also simplifies the printing process. Many businesses find this efficient and effective for their operations.
However, as technology advances, some question whether these machines can keep up with sustainability demands. The production of thermal paper itself raises environmental concerns. Thus, while the Thermal Paper Machine offers numerous benefits, there are still challenges to address. Balancing efficiency with eco-friendliness is essential for the future of this industry.

Thermal paper is a specialized paper that reacts to heat, creating an image or text. It is coated with a thermal-sensitive layer. This layer changes color when exposed to a heat source, such as a thermal printer. Commonly, you’ll find thermal paper in point-of-sale systems, cash registers, and credit card terminals.
Many businesses rely on thermal paper for receipts and labels. It’s quick and efficient. Users appreciate its immediate results. However, there are drawbacks. The printed information can fade over time due to heat and light exposure. This makes it less ideal for long-term record-keeping.
Additionally, not all thermal paper is created equal. Some types may smudge or lose clarity quickly. It’s worth considering the quality of the thermal paper chosen. Overall, while thermal paper offers convenience, users must be mindful of its limitations. Balancing benefits with potential issues is crucial for effective use.
This chart displays the annual production volume of thermal paper in metric tons alongside its common applications in percentage. The data illustrates the demand and usage of thermal paper across different sectors.
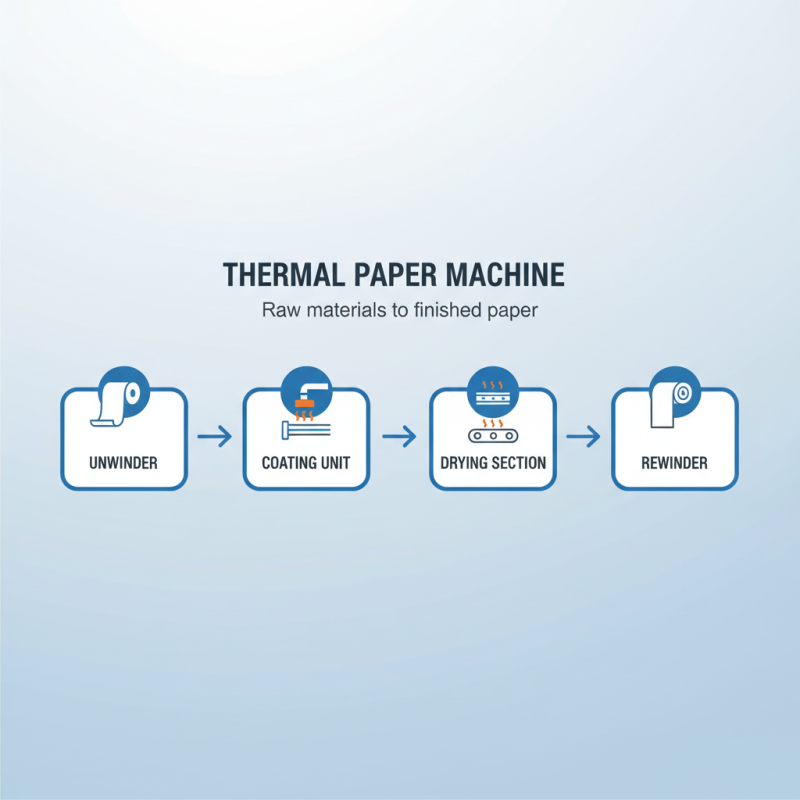
A thermal paper machine is designed to produce thermal paper, commonly used in receipts and labels. The main components of this machine include the unwinder, coating unit, drying section, and rewinder. Each part plays a crucial role in transforming raw materials into finished thermal paper.
The unwinder feeds the base paper into the machine. It must operate smoothly to avoid jams. The coating unit applies the thermal layer. This layer reacts to heat, allowing images and text to appear when printed. Inadequate coating can lead to poor print quality.
After coating, the drying section removes moisture. It must reach the right temperature for effective drying. If not, the paper can get damaged or discolored. The final rewinder rolls the finished paper, ready for distribution. It's essential to regularly check all components to ensure they function correctly.
Tips: Regular maintenance can enhance machine performance. Monitor the condition of the heating elements; they are vital for the coating unit's effectiveness. Also, inspect the rolls for any defects, as they can cause issues during printing.
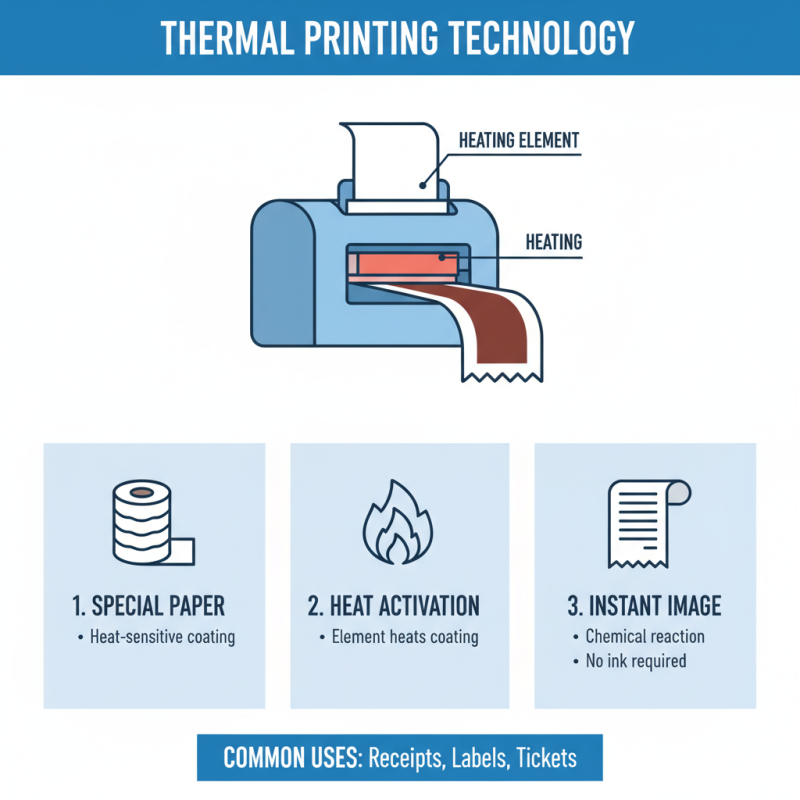
Thermal paper machines are specialized printers designed to create images through heat. The process begins with a heating element that activates a special coating on thermal paper. When the paper passes over this heated component, it produces a visible image. This technology is widely used for receipts and labels.
The mechanism is simple but effective. As the paper feeds through the machine, it encounters a thermal print head. This head consists of tiny elements that generate heat. The temperature varies depending on the image needed. High heat creates dark images, while lower heat yields lighter shades. This precision is crucial for legibility.
Despite its advantages, this method does have drawbacks. For example, thermal prints can fade over time, especially with exposure to heat and light. Users need to store printed items carefully to preserve them. Additionally, understanding how to maintain the machine can be challenging. Regular cleaning is necessary to ensure optimal performance. A simple oversight can lead to print quality issues.
Thermal paper machines offer several advantages that make them increasingly popular in various industries. The ability to print without ink is a key selling point. This technology uses heat to create an image directly on the paper. It simplifies operations, minimizing the need for extra supplies. However, users must ensure the thermal printouts are protected from heat and light; otherwise, they may fade quickly.
Another benefit is the cost-effectiveness of thermal paper machines. Businesses can save money on printing supplies. Ink and toner can be expensive, leading to higher running costs. By utilizing thermal printing, companies can reduce these expenses significantly. Still, the initial investment in a thermal paper machine can be daunting for small businesses. They need to weigh potential savings against upfront costs.
Additionally, thermal paper machines are compact and straightforward to use. They require less maintenance compared to traditional printers. This ease of use helps reduce downtime. On the flip side, businesses can face challenges with compatibility and paper quality. Ensuring the paper stock is appropriate for the machine is crucial for optimal performance. Users often overlook this, leading to frustrating printing issues.
| Feature | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Prints documents quickly due to direct thermal transfer. | Increases productivity and reduces wait times. |
| Print Quality | Produces sharp and clear images and text. | Enhances the professionalism of printed materials. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Lower operating costs as there is no need for ink or toner. | Reduces overall printing expenses. |
| Compact Design | Often smaller than traditional printers, making them space-efficient. | Ideal for retail and mobile usage. |
| Versatility | Can print on various formats such as labels, tickets, and receipts. | Adaptable for different business needs. |
Thermal paper machines are crucial in various industries. Regular maintenance ensures they function seamlessly. Keeping the rollers clean is essential. In fact, studies show that 70% of printing issues stem from dirty components. Letting dust build up can lead to inconsistent print quality. It’s a headache most operators can avoid with routine checks.
Troubleshooting becomes necessary when problems arise. Paper jams are common, often due to improper loading. Operators should check for misalignment. A quick inspection can save time. Additionally, heat settings can affect the print output. If colors appear faded, recalibrating the heat can improve results significantly. Data from industry reports indicate that optimal heat settings can enhance print durability by over 30%.
Operators should note that not every issue has a clear solution. Some problems may require more in-depth analysis. For instance, frequent thermal paper curling might indicate humidity issues in the environment. Regular monitoring of machine performance is vital, but not always practiced. Operators sometimes overlook small anomalies, which can grow into larger malfunctions. Understanding these nuances can lead to better operational efficiency.
